Health and Safety
HEALTH AND SAFETY
Introduction
This section outlines the basic minimum health and safety requirements for conducting in-person retrofit advice visits in domestic dwellings.
All organisations participating in LEAD are responsible for ensuring that its employees, contractors, and representatives are aware and adhere to the health and safety requirements outlined in this code of conduct.
By adhering to the guidelines outlined in this section, LEAD aims to create a safe and secure environment for employees and residents participating in the service. In rare cases where full Risk Assessment is required, a more in-depth questionnaire together with common risks and relevant regulations is provided in Appendix XXXX
Health and Safety risk management:
Health and safety risk management is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential hazards and risks within a workplace or any environment to safeguard the health, safety, and wellbeing of individuals. It involves a proactive approach to anticipate and address hazards before they result in harm, injury, or damage. Risk management entails identifying various types of hazards. Evaluating their likelihood and potential consequences and implementing appropriate control measures to reduce or eliminate risks. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and review are essential to ensure the effectiveness of control measures and identify any emerging risks or changes in the environment. By effectively managing health and safety risks, all organisations involved can create a safe and secure environment for employees and residents participating in the service.
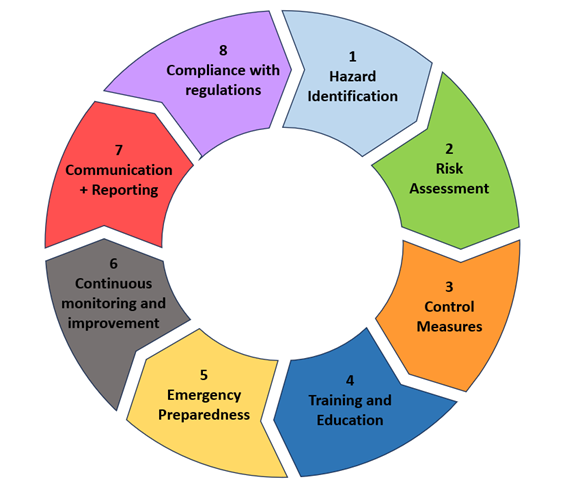
1. Hazard Identification
· Conduct a visual inspection of the domestic dwelling to identify existing hazards and potential risks.
· Document all hazards observed during the inspection
2. Risk Assessment:
· Assess the severity and likelihood of each identified hazard.
3. Mitigation and Control Measures:
· Develop and implement control measures to mitigate identified health and safety hazards, including recommendations for mitigation or elimination.
4. Training and education:
· All individuals participating in LEAD retrofit advice visits must receive comprehensive and up-to-date training on health and safety protocols, including hazard identification, risk assessment and emergency procedures.
5. Emergency preparedness:
· Establish emergency preparedness plans and procedures to address potential health and safety incidents. This includes access to first aid supplies, and protocols for internal/external reporting and responding to emergencies.
· Maintain emergency contact information for relevant authorities, medical services, and other emergency responders.
6. Continuous monitoring and improvement:
· Continuously monitor the effectiveness of control measures and review risk assessments periodically.
· Stay updated on industry best practices and regulatory requirements to adapt health and safety protocols accordingly
7. Communication and reporting:
· A clear process should be established for reporting accidents, incidents, and near misses.
· All reported incidents should be thoroughly investigated to determine root causes and prevent recurrence.
· Employees should be encouraged to report hazards and contribute to continuous improvement for safety protocols.
8. Compliance with regulations:
· All organisations will comply with all relevant health and safety regulations and standards.
(Common health and Safety risks and relevant regulations can be found in appendix XXXX)
· Regular audits will be conducted to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: Retrofit Advice Visits
Pre-visit:
- Advisors should engage with the HO prior to the retrofit advice visit to gather information about the property and occupants as well as any specific concerns or hazards they may be aware of. E.g. vulnerable person(s), property condition
- Utilize online mapping tools and property databases to gather information about the location and surroundings of the dwelling
- Review any existing information/public records related to the property, such as building permits, environmental assessments, utility information.
- Document findings from the desk assessment, including identified hazards, concerns, and recommended actions.
During the Visit:
- Control measures should be implemented to mitigate identified health and safety hazards, including recommendations for mitigation or elimination.
- HO should be made aware of any issues that have an impact on their safety and that of others.
- Any variations or newly identified risks should be assessed, and appropriate controls actioned without delay.